Arachidonic acid
Template:Short description Template:Cs1 config Template:Chembox
Arachidonic acid (AA, sometimes ARA) is a polyunsaturated omega−6 fatty acid 20:4(ω−6), or 20:4(5,8,11,14).<ref name="lpi">Template:Cite web</ref><ref>Template:Cite web</ref> It is a precursor in the formation of leukotrienes, prostaglandins, and thromboxanes.<ref name=Dorland>Template:Cite web</ref>
Together with omega−3 fatty acids and other omega−6 fatty acids, arachidonic acid provides energy for body functions, contributes to cell membrane structure, and participates in the synthesis of eicosanoids, which have numerous roles in physiology as signaling molecules.<ref name=lpi/><ref name="ods">Template:Cite web</ref>
Its name derives from the ancient Greek neologism arachis 'peanut', although peanut oil does not contain any arachidonic acid.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Arachidonate is the name of the derived carboxylate anion (conjugate base of the acid), salts, and some esters.
Chemistry
In chemical structure, arachidonic acid is a carboxylic acid with a 20-carbon chain and four cis-double bonds; the first double bond is located at the sixth carbon from the omega end.
Some chemistry sources define 'arachidonic acid' to designate any of the eicosatetraenoic acids. However, almost all writings in biology, medicine, and nutrition limit the term to all cis-5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid.
Biology
Arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated fatty acid present in the phospholipids (especially phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, and phosphatidylinositides) of membranes of the body's cells, and is abundant in the brain, muscles, and liver. Skeletal muscle is an especially active site of arachidonic acid retention, accounting for roughly 10–20% of the phospholipid fatty acid content typically.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
In addition to being involved in cellular signaling as a lipid second messenger involved in the regulation of signaling enzymes, such as PLC-γ, PLC-δ, and PKC-α, -β, and -γ isoforms, arachidonic acid is a key inflammatory intermediate and can also act as a vasodilator.<ref name=Dominiczak>Template:Cite book</ref> (Note separate synthetic pathways, as described in section below.)
Biosynthesis and cascade in humans
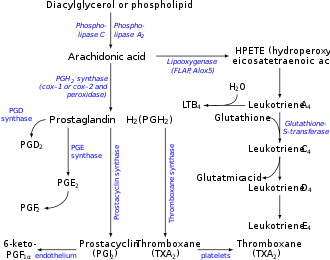
Arachidonic acid is freed from phospholipids by hydrolysis, catalyzed by the phospholipase A2 (PLA2).<ref name=Dominiczak/>
Arachidonic acid for signaling purposes appears to be derived by the action of group IVA cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2, 85 kDa), whereas inflammatory arachidonic acid is generated by the action of a low-molecular-weight secretory PLA2 (sPLA2, 14-18 kDa).<ref name=Dominiczak/>
Arachidonic acid is a precursor to a wide range of eicosanoids:
- The enzymes cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 (i.e. prostaglandin G/H synthase 1 and 2 [PTGS1 and PTGS2]) convert arachidonic acid to prostaglandin G2 and prostaglandin H2, which in turn may be converted to various prostaglandins, to prostacyclin, to thromboxanes, and to the 17-carbon product of thromboxane metabolism of prostaglandin G2/H2, 12-hydroxyheptadecatrienoic acid (12-HHT).<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- The enzyme 5-lipoxygenase catalyzes the oxidation of arachidonic acid to 5-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HPETE), which in turn converts to various leukotrienes (i.e., leukotriene B4, leukotriene C4, leukotriene D4, and leukotriene E4) as well as to 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HETE) which may then be further metabolized to 5-HETE's more potent 5-keto analog, 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid (5-oxo-ETE) (also see 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid).<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- The enzymes 15-lipoxygenase-1 (ALOX15) and 15-lipoxygenase-2 (ALOX15B). ALOX15B catalyzes the oxidation of arachidonic acid to 15-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15-HPETE), which may then be further converted to 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (15-HETE) and lipoxins;<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> 15-Lipoxygenase-1 may also further metabolize 15-HPETE to eoxins in a pathway analogous to (and presumably using the same enzymes as used in) the pathway which metabolizes 5-HPETE to leukotrienes.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- The enzyme 12-lipoxygenase (ALOX12) catalyzes oxidation of arachidonic acid to 12-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HPETE), which may then be metabolized to 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) and to hepoxilins.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- Arachidonic acid is also a precursor to anandamide.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- Some arachidonic acid is converted into hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs) and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) by epoxygenase.<ref name=boron108>Template:Cite book</ref>
The production of these derivatives and their actions in the body are collectively known as the "arachidonic acid cascade"; see Essential fatty acid interactions and the enzyme and metabolite linkages given in the previous paragraph for more details.
PLA2 activation
Template:Further PLA2, in turn, is activated by ligand binding to receptors, including:
- 5-HT2 receptors <ref name=boron103>Template:Cite book</ref>
- mGLUR1<ref name=boron103/>
- bFGF receptor<ref name=boron103/>
- IFN-α receptor<ref name=boron103/>
- IFN-γ receptor<ref name=boron103/>
Furthermore, any agent increasing intracellular calcium may cause activation of some forms of PLA2.<ref name=boron104/>
PLC activation
Template:Further Alternatively, arachidonic acid may be cleaved from phospholipids after phospholipase C (PLC) cleaves off the inositol trisphosphate group, yielding diacylglycerol (DAG), which subsequently is cleaved by DAG lipase to yield arachidonic acid.<ref name=boron103/>
Receptors that activate this pathway include:
- A1 receptor<ref name=boron104>Template:Cite book</ref>
- D2 receptor<ref name=boron104/>
- α2 adrenergic receptor<ref name=boron104/>
- 5-HT1 receptor<ref name=boron104/>
PLC may also be activated by MAP kinase. Activators of this pathway include PDGF and FGF.<ref name=boron104/>
In the body
Cell membranes
Along with other omega−6 and omega−3 fatty acids, arachidonic acid contributes to the structure of cell membranes.<ref name=lpi/> When incorporated into phospholipids, the omega fatty acids affect cell membrane properties, such as permeability and the activity of enzymes and cell-signaling mechanisms.<ref name=lpi/>
Brain
Arachidonic acid, one of the most abundant fatty acids in the brain, is present in similar quantities to docosahexaenoic acid, with the two accounting for about 20% of brain fatty-acid content.<ref>Template:Cite book</ref> Arachidonic acid is involved in the early neurological development of infants.<ref name="crawford">Template:Cite journal</ref>
Dietary supplement
Template:Missing information Arachidonic acid is marketed as a dietary supplement.<ref name=lpi/><ref name=ods/> A 2019 review of clinical studies investigating the potential health effects of arachidonic acid supplementation of up to 1500 mg per day on human health found there were no clear benefits.<ref name="calder">Template:Cite journal</ref> There were no adverse effects in adults of using high daily doses (1500 mg) of arachidonic acid on several biomarkers of blood chemistry, immune function, and inflammation.<ref name=calder/>
A 2009 review indicated that consumption of 5−10% of food energy from omega−6 fatty acids including arachidonic acid may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases compared to lower intakes.<ref name =Harris>Template:Cite journal</ref> A 2014 meta-analysis of possible associations between heart disease risk and individual fatty acids reported a significantly reduced risk of heart disease with higher levels of EPA, DHA, and arachidonic acid.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
See also
- Aspirin—inhibits cyclooxygenase enzyme, preventing conversion of arachidonic acid to other signal molecules
- Docosadienoic acid
- Fish oil
- Juniperonic acid, an isomer
- Polyunsaturated fat
References
External links
Template:Eicosanoids Template:Fatty acids Template:Navboxes Template:Authority control