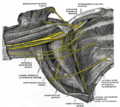
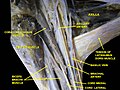
Brachial artery
Template:Short description Template:Use American English Template:Use mdy dates Template:More footnotes Template:Infobox artery
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital fossa at the elbow. It then divides into the radial and ulnar arteries which run down the forearm.<ref name=":0">Template:Cite book</ref><ref>Template:Cite web</ref> In some individuals, the bifurcation occurs much earlier and the ulnar and radial arteries extend through the upper arm. The pulse of the brachial artery is palpable on the anterior aspect of the elbow, medial to the tendon of the biceps, and, with the use of a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff), often used to measure the blood pressure.<ref name=":0" />
The brachial artery is closely related to the median nerve; in proximal regions, the median nerve is immediately lateral to the brachial artery.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Distally, the median nerve crosses the medial side of the brachial artery and lies anterior to the elbow joint.<ref name=":0" /><ref name=":1">Template:Cite book</ref>
Structure
The brachial artery gives rise to the following branches:<ref name=":1" />
- Profunda brachii artery (deep brachial artery)
- Superior ulnar collateral artery
- Inferior ulnar collateral artery
- Radial artery (used to palpate radial pulse)(a terminal branch)
- Ulnar artery (a terminal branch)
- Nutrient branches to the humerus
It also gives rise to important anastomotic networks of the elbow and (as the axillary artery) the shoulder.
The biceps head is lateral to the brachial artery. The median nerve is medial to the brachial artery for most of its course. fracture of lower end of humerous may cause rupture of bracheal artery
Additional images
-
Cross-section through the middle of upper arm
-
The axillary artery and its branches
-
The radial and ulnar arteries
-
Ulnar and radial arteries; deep view
-
The deep veins of the upper extremity
-
The right brachial plexus (infraclavicular portion) in the axillary fossa; viewed from below and in front
-
Front of right upper extremity, showing surface markings for bones, arteries, and nerves
-
Deep dissection; anterior view
-
Deep dissection; anterior view
-
The brachial artery can be palpated midway along the medial side of the arm
-
A medical student using a sphygmomanometer to measure blood pressure from the brachial artery's pulse.
See also
- Femoral artery, a leg-based artery with a similar function
References
External links
- Dissection at mvm.ed.ac.uk
- Image at umich.edu – pulse (archived 6 December 2006)
- Template:NormanAnatomy