Nitrogen oxide
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Template:For Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
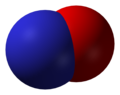
- Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
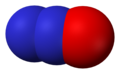
- Nitrogen dioxide (Template:Chem2), nitrogen(IV) oxide
- Nitrogen trioxide (Template:Chem2), or nitrate radical
- Nitrous oxide (Template:Chem2), nitrogen(0,II) oxide
- Dinitrogen dioxide (Template:Chem2), nitrogen(II) oxide dimer
- Dinitrogen trioxide (Template:Chem2), nitrogen(II,IV) oxide
- Dinitrogen tetroxide (Template:Chem2), nitrogen(IV) oxide dimer
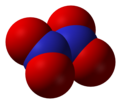
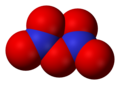
- Dinitrogen pentoxide (Template:Chem2), nitrogen(V) oxide, or nitronium nitrate Template:Chem2
- Nitrosyl azide (Template:Chem2), nitrogen(−I,0,I,II) oxide
- Nitryl azide (Template:Chem2)
- Oxatetrazole (Template:Chem2)
- Trinitramide (Template:Chem2 or Template:Chem2), nitrogen(0,IV) oxide
Anions
Cations
Atmospheric sciences
- [[NOx|Template:Chem2]] (or NOx) refers to the sum of NO and [[nitrogen dioxide|Template:Chem2]].<ref>United States Clean Air Act, Template:USC</ref><ref>
Template:Citation </ref>
- [[NOy|Template:Chem2]] (or NOy) refers to the sum of Template:Chem2 and all oxidized atmospheric odd-nitrogen species (e.g. the sum of Template:Chem2, [[Nitric acid|Template:Chem2]], [[Nitrous acid|Template:Chem2]], etc.)
- Template:Chem2 (or NOz) = Template:Chem2 − Template:Chem2
- Mixed Oxides of Nitrogen ("MON"): solutions of nitric oxide in dinitrogen tetroxide/nitrogen dioxide.
-
style }}
-
style }}
-
style }}
-
style }}
-
style }}
-
style }}
-
style }}
Stability
Due to relatively weak N–O bonding, all nitrogen oxides are unstable with respect to Template:Chem2 and Template:Chem2, which is the principle behind the catalytic converter, and prevents the oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere from combusting.
See also
- Nitrate
- Nitrogen oxide sensor
- Sulfur nitrides, which are valence isoelectronic with nitrogen oxides