Orthorhombic crystal system
Template:Short description In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (a by b) and height (c), such that a, b, and c are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal.
Bravais lattices
There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic.
| Bravais lattice | Primitive orthorhombic |
Base-centered orthorhombic |
Body-centered orthorhombic |
Face-centered orthorhombic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson symbol | oP | oS | oI | oF |
| Unit cell | Orthohombic, simple | Orthohombic, base-centered | Orthohombic, body-centered | Orthohombic, face-centered |
For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;<ref>See Template:Harvp, row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90°</ref> it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length <math>a</math> of the primitive cell below equals <math>\frac{1}{2} \sqrt{a^2+b^2}</math> of the conventional cell above.
Crystal classes
Template:Further The orthorhombic crystal system class names, examples, Schönflies notation, Hermann-Mauguin notation, point groups, International Tables for Crystallography space group number,<ref name="ITC">Template:Cite book</ref> orbifold notation, type, and space groups are listed in the table below.
| [[Space group#Notation|Template:Abbr]] | Point group | Type | Example | Space groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> | Schön. | Intl | Orb. | Cox. | Primitive | Base-centered | Face-centered | Body-centered | |||
| 16–24 | Rhombic disphenoidal | D2 (V) | 222 | 222 | [2,2]+ | Enantiomorphic | Epsomite
Boron (gamma form) |
P222, P2221, P21212, P212121 | C2221, C222 | F222 | I222, I212121 |
| 25–46 | Rhombic pyramidal | C2v | mm2 | *22 | [2] | Polar | Hemimorphite, bertrandite | Pmm2, Pmc21, Pcc2, Pma2, Pca21, Pnc2, Pmn21, Pba2, Pna21, Pnn2 | Cmm2, Cmc21, Ccc2 Amm2, Aem2, Ama2, Aea2 |
Fmm2, Fdd2 | Imm2, Iba2, Ima2 |
| 47–74 | Rhombic dipyramidal | D2h (Vh) | mmm | *222 | [2,2] | Centrosymmetric | Olivine, aragonite, marcasite | Pmmm, Pnnn, Pccm, Pban, Pmma, Pnna, Pmna, Pcca, Pbam, Pccn, Pbcm, Pnnm, Pmmn, Pbcn, Pbca, Pnma | Cmcm, Cmce, Cmmm, Cccm, Cmme, Ccce | Fmmm, Fddd | Immm, Ibam, Ibca, Imma |
In two dimensions
Template:Main In two dimensions there are two orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive rectangular and centered rectangular.
| Bravais lattice | Rectangular | Centered rectangular |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson symbol | op | oc |
| Unit cell | 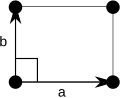
|
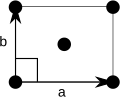
|