Renal cell carcinoma
Template:Short description {{#invoke:other uses|otheruses}} Template:More medical citations needed Template:Infobox medical condition Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, responsible for approximately 90–95% of cases.<ref name=MSR>Template:Cite web</ref> It is more common in men (with a male-to-female ratio of up to 2:1).<ref name=EAU2023>Template:Cite book</ref> It is most commonly diagnosed in the elderly (especially in people over 75 years of age).<ref name=Znaor2015>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Initial treatment is most commonly either partial or complete removal of the affected kidney(s).<ref name="r">Template:Cite journal</ref> Where the cancer has not metastasised (spread to other organs) or burrowed deeper into the tissues of the kidney, the five-year survival rate is 65–90%,<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> but this is lowered considerably when the cancer has spread.
The body is remarkably good at hiding the symptoms and as a result people with RCC often have advanced disease by the time it is discovered.<ref name="path">Template:Cite book</ref> The initial symptoms of RCC often include blood in the urine (occurring in 40% of affected persons at the time they first seek medical attention), flank pain (40%), a mass in the abdomen or flank (25%), weight loss (33%), fever (20%), high blood pressure (20%), night sweats and generally feeling unwell.<ref name="MSR" /> When RCC metastasises, it most commonly spreads to the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, adrenal glands, brain or bones.<ref name = MM/> Immunotherapy and targeted therapy have improved the outlook for metastatic RCC.<ref name=singer>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref name=":0">Template:Cite journal</ref>
RCC is also associated with a number of paraneoplastic syndromes (PNS) which are conditions caused by either the hormones produced by the tumour or by the body's attack on the tumour and are present in about 20% of those with RCC.<ref name="MSR" /> These syndromes most commonly affect tissues which have not been invaded by the cancer.<ref name="MSR" /> The most common PNSs seen in people with RCC are: high blood calcium levels, high red blood cell count, high platelet count and secondary amyloidosis.<ref name = MM/> Template:TOC limit
Signs and symptoms
Historically, medical practitioners expected a person to present with three findings. This classic triad<ref name="cohen" /> is 1: haematuria, which is when there is blood present in the urine, 2: flank pain, which is pain on the side of the body between the hip and ribs, and 3: an abdominal mass, similar to bloating but larger. It is now known that this classic triad of symptoms only occurs in 10–15% of cases, and is usually indicative that the renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is in an advanced stage.<ref name="cohen" /> Today, renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is often asymptomatic, meaning it presents no symptoms, and is commonly detected incidentally during examinations for unrelated medical conditions. The percentage of asymptomatic and incidentally diagnosed RCC cases, particularly smaller tumors, has continued to rise in recent years.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Other signs and symptom may include haematuria;<ref name="cohen" /> loin pain;<ref name="cohen" /> abdominal mass;<ref name="motzer" /> malaise, which is a general feeling of unwellness;<ref name="motzer" /> weight loss and/or loss of appetite;<ref name="kim" /> anaemia resulting from depression of erythropoietin;<ref name="cohen" /> erythrocytosis (increased production of red blood cells) due to increased erythropoietin secretion;<ref name="cohen" /> varicocele, which is seen in males as an enlargement of the pampiniform plexus of veins draining the testis (more often the left testis)<ref name="motzer" /> hypertension (high blood pressure) resulting from secretion of renin by the tumour;<ref name="Birkhauser2013" /> hypercalcemia, which is elevation of calcium levels in the blood;<ref name="LaneBook" /> sleep disturbance or night sweats;<ref name="kim" /> recurrent fevers;<ref name="kim" /> and chronic fatigue.<ref name="metz" />
Risk factors
Lifestyle
The greatest risk factors for RCC are lifestyle-related: smoking, obesity and hypertension (high blood pressure) have been estimated to account for up to 50% of cases.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Occupational exposure to some chemicals such as asbestos, cadmium, lead, chlorinated solvents, petrochemicals and PAH (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon) has been examined by multiple studies with inconclusive results.<ref name="Ljungberg et al 2011" /><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Another suspected risk factor is the long term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS).<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Finally, studies have found that women who have had a hysterectomy are at more than double the risk of developing RCC than those who have not.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Moderate alcohol consumption, on the other hand, has been shown to have a protective effect.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Genetics
Hereditary factors have a minor impact on individual susceptibility with immediate relatives of people with RCC having a two to fourfold increased risk of developing the condition.<ref name="Lipworth2009" /> Other genetically linked conditions also increase the risk of RCC, including hereditary papillary renal carcinoma, hereditary leiomyomatosis, Birt–Hogg–Dube syndrome, hyperparathyroidism-jaw tumor syndrome, familial papillary thyroid carcinoma, von Hippel–Lindau disease<ref name="Pavlovich2004" /> and sickle cell disease.<ref name="rini" />
The most significant disease affecting risk however is not genetically linked – patients with acquired cystic disease of the kidney requiring dialysis are 30 times more likely than the general population to develop RCC.<ref name="Baldewijns2008" />
Pathophysiology
The tumour arises from the cells of the proximal renal tubular epithelium.<ref name = MSR/> It is considered an adenocarcinoma.<ref name=MM>Template:Cite web</ref> There are two subtypes: sporadic (that is, non-hereditary) and hereditary.<ref name = MSR/> Both such subtypes are associated with mutations in the short-arm of chromosome 3, with the implicated genes being either tumour suppressor genes (VHL and TSC) or oncogenes (like c-Met).<ref name = MSR/>
Diagnosis
The first steps taken to diagnose this condition are consideration of the signs and symptoms, and a medical history (the detailed medical review of past health state) to evaluate any risk factors. Based on the symptoms presented, a range of biochemical tests (using blood and/or urine samples) may also be considered as part of the screening process to provide sufficient quantitative analysis of any differences in electrolytes, kidney and liver function, and blood clotting times.<ref name="rini" /> Upon physical examination, palpation of the abdomen may reveal the presence of a mass or an organ enlargement.<ref name=Tjaden>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Although this disease lacks characterization in the early stages of tumor development, considerations based on diverse clinical manifestations, as well as resistance to radiation and chemotherapy are important. The main diagnostic tools for detecting renal cell carcinoma are ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scanning and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the kidneys.<ref name=agabegi2nd>Template:Cite book</ref>
Classification
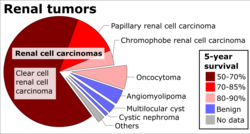
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is not a single entity, but rather a collection of different types of tumours, each derived from the various parts of the nephron (epithelium or renal tubules) and possessing distinct genetic characteristics, histological features, and, to some extent, clinical phenotypes.<ref name="rini" />
| Classification of the Common Histological Subtypes of Renal Cell Carcinoma<ref name=rini /> | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Renal Cell Carcinoma Subtype | Frequency | Genetic Abnormalities | Characteristics |
|
Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma (CCRCC)  |
60–70% |
|
|
Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma (PRCC)
 |
10–15% |
|
|
Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma (ChRCC)
 |
3–5% |
|
|
| Clinical, Pathological and Genetic Features of Uncommon RCC Subtypes Included in the 2004 WHO Classification of RCC Pathology<ref name=zhou /><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCC subtype | Clinical features | Cell/Tissue Characteristics | Genetics | Prognosis |
| Multilocular Cystic RCC |
|
Clear cytoplasm, small dark nuclei | 3p deletion as observed in CCRCC |
|
| Carcinoma of the Collecting Ducts of Bellini |
|
High-grade tumor cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm | Variable results: LOH on chromosomes 1q, 6p, 8p,9p, 13q, 19q32 and 21q; c-erB2 amplification associated with unfavorable outcome |
|
| Medullary Carcinoma |
|
Haemorrhage and necrosis, high-grade tumour cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm | Not well defined |
|
| Xp11.2 Translocation Carcinoma |
|
|
Chromosomal translocation involving TFE3 gene on Xp11.2 resulting in overexpression of the TFE3 protein |
|
| Mucinous Tubular Spindle Cell Carcinoma |
|
Tubules, extracellular mucin and spindle cells | Not well defined; Losses involving chromosomes 1, 4, 6, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15, 18, 22 reported; 3p alterations and gain of chromosome 7, and 17 not present |
|
| Post-Neuroblastoma Renal Cell Carcinoma |
|
Eosinophilic cells with oncocytoid features (same as CCRCC) | Not well defined; Loss of multiple chromosomal loci observed | Similar to other common RCC subtypes |
Array-based karyotyping can be used to identify characteristic chromosomal aberrations in renal tumors with challenging morphology.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Array-based karyotyping performs well on paraffin embedded tumours<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> and is amenable to routine clinical use. See also Virtual Karyotype for CLIA certified laboratories offering array-based karyotyping of solid tumours.
The 2004 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of genitourinary tumours recognizes over 40 subtypes of renal neoplasms. Since the publication of the latest iteration of the WHO classification in 2004, several novel renal tumour subtypes have been described:<ref name="pmid24364021">Template:Cite journal</ref>
- Clear cell papillary renal cell carcinoma and clear cell renal cell carcinoma with smooth muscle stroma<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- Mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma (MTSCC) <ref name="pmid24364021"/>
- Multilocular cystic clear cell renal cell carcinoma<ref name="pmid24364021"/>
- Tubulocystic renal cell carcinoma
- Thyroid-like follicular renal cell carcinoma
- Acquired cystic kidney disease-associated renal cell carcinoma
- Renal cell carcinoma with t(6;11) translocation (TFEB)
- Hybrid oncocytoma/chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell carcinoma (HLRCC)
Laboratory tests
Laboratory tests are generally conducted when the patient presents with signs and symptoms that may be characteristic of kidney impairment. They are not primarily used to diagnose kidney cancer, due to its asymptomatic nature and are generally found incidentally during tests for other illnesses such as gallbladder disease.<ref name=Wood>Template:Cite journal</ref> In other words, these cancers are not detected usually because they do not cause pain or discomfort when they are discovered. Laboratory analysis can provide an assessment on the overall health of the patient and can provide information in determining the staging and degree of metastasis to other parts of the body (if a renal lesion has been identified) before treatment is given.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
Urine analysis
The presence of blood in urine is a common presumptive sign of renal cell carcinoma. The haemoglobin of the blood causes the urine to be rusty, brown or red in colour. Alternatively, urinalysis can test for sugar, protein and bacteria which can also serve as indicators for cancer. A complete blood cell count can also provide additional information regarding the severity and spreading of the cancer.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Complete blood cell count
The CBC provides a quantified measure of the different cells in the whole blood sample from the patient. Such cells examined for in this test include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes) and platelets (thrombocytes). A common sign of renal cell carcinoma is anaemia whereby the patient exhibits deficiency in red blood cells.<ref name=Johann>Template:Cite journal</ref> CBC tests are vital as a screening tool for examination the health of patient prior to surgery. Inconsistencies with platelet counts are also common amongst these cancer patients and further coagulation tests, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) should be considered.<ref name="Access Anytime Anywhere">Template:Cite web</ref>
Blood chemistry
Blood chemistry tests are conducted if renal cell carcinoma is suspected as cancer has the potential to elevate levels of particular chemicals in blood. For example, liver enzymes such as aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) are found to be at abnormally high levels.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> The staging of the cancer can also be determined by abnormal elevated levels of calcium, which suggests that the cancer may have metastasised to the bones.<ref name="Motzer2003">Template:Cite journal</ref> In this case, a doctor should be prompted for a CT scan. Blood chemistry tests also assess the overall function of the kidneys and can allow the doctor to decide upon further radiological tests.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
Radiology
The characteristic appearance of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a solid renal lesion which disturbs the renal contour. It will frequently have an irregular or lobulated margin and may be seen as a lump on the lower pelvic or abdomen region. Traditionally, 85 to 90% of solid renal masses will turn out to be RCC but cystic renal masses may also be due to RCC.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> However, the advances of diagnostic modalities are able to incidentally diagnose a great proportion of patients with renal lesions that may appear to be small in size and of benign state. Ten percent of RCC will contain calcifications, and some contain macroscopic fat (likely due to invasion and encasement of the perirenal fat).<ref name=Nakada>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Deciding on the benign or malignant nature of the renal mass on the basis of its localized size is an issue as renal cell carcinoma may also be cystic. As there are several benign cystic renal lesions (simple renal cyst, haemorrhagic renal cyst, multilocular cystic nephroma, polycystic kidney disease), it may occasionally be difficult for the radiologist to differentiate a benign cystic lesion from a malignant one.<ref name="Pattamapaspong">Template:Cite journal</ref> The Bosniak classification system for cystic renal lesions classifies them into groups that are benign and those that need surgical resection, based on specific imaging features.<ref name="Israel">Template:Cite journal</ref>
The main imaging tests performed in order to identify renal cell carcinoma are pelvic and abdominal CT scans, ultrasound tests of the kidneys (ultrasonography), MRI scans, intravenous pyelogram (IVP) or renal angiography.<ref name=Jubelirer>Template:Cite journal</ref> Among these main diagnostic tests, other radiologic tests such as excretory urography, positron-emission tomography (PET) scanning, ultrasonography, arteriography, venography, and bone scanning can also be used to aid in the evaluation of staging renal masses and to differentiate non-malignant tumours from malignant tumours.<ref name="Access Anytime Anywhere"/>
Computed tomography
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) scanning is routinely used to determine the stage of the renal cell carcinoma in the abdominal and pelvic regions. CT scans have the potential to distinguish solid masses from cystic masses and may provide information on the localization, stage or spread of the cancer to other organs of the patient. Key parts of the human body which are examined for metastatic involvement of renal cell carcinoma may include the renal vein, lymph node and the involvement of the inferior vena cava.<ref name=Beck>Template:Cite journal</ref> According to a study conducted by Sauk et al., multidetector CT imaging characteristics have applications in diagnosing patients with clear renal cell carcinoma by depicting the differences of these cells at the cytogenic level.<ref name=Sauk>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Ultrasound
Ultrasonographic examination can be useful in evaluating questionable asymptomatic kidney tumours and cystic renal lesions if computed tomography imaging is inconclusive. This safe and non-invasive radiologic procedure uses high frequency sound waves to generate an interior image of the body on a computer monitor. The image generated by the ultrasound can help diagnose renal cell carcinoma based on the differences of sound reflections on the surface of organs and the abnormal tissue masses. Essentially, ultrasound tests can determine whether the composition of the kidney mass is mainly solid or filled with fluid.<ref name="Jubelirer" />
A percutaneous biopsy can be performed by a radiologist using ultrasound or computed tomography to guide sampling of the tumour for the purpose of diagnosis by pathology. However this is not routinely performed because when the typical imaging features of renal cell carcinoma are present, the possibility of an incorrectly negative result together with the risk of a medical complication to the patient may make it unfavourable from a risk-benefit perspective.<ref name=Lane>Template:Cite journal</ref> However, biopsy tests for molecular analysis to distinguish benign from malignant renal tumours is of investigative interest.<ref name="Lane" />
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans provide an image of the soft tissues in the body using radio waves and strong magnets. MRI can be used instead of CT if the patient exhibits an allergy to the contrast media administered for the test.<ref name=Hricak>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref name=Janus>Template:Cite journal</ref> Sometimes prior to the MRI scan, an intravenous injection of a contrasting material called gadolinium is given to allow for a more detailed image. Patients on dialysis or those who have renal insufficiency should avoid this contrasting material as it may induce a rare, yet severe, side effect known as nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.<ref name=Nishimura>Template:Cite journal</ref> A bone scan or brain imaging is not routinely performed unless signs or symptoms suggest potential metastatic involvement of these areas. MRI scans should also be considered to evaluate tumour extension which has grown in major blood vessels, including the vena cava, in the abdomen. MRI can be used to observe the possible spread of cancer to the brain or spinal cord should the patient present symptoms that suggest this might be the case.Template:Citation needed
Intravenous pyelogram
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is a useful procedure in detecting the presence of abnormal renal mass in the urinary tract. This procedure involves the injection of a contrasting dye into the arm of the patient. The dye travels from the blood stream and into the kidneys which in time, passes into the kidneys and bladder. This test is not necessary if a CT or MRI scan has been conducted.<ref name=Reznek>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Renal angiography
Renal angiography uses the same principle as IVP, as this type of X-ray also uses a contrasting dye. This radiologic test is important in diagnosing renal cell carcinoma as an aid for examining blood vessels in the kidneys. This diagnostic test relies on the contrasting agent which is injected in the renal artery to be absorbed by the cancerous cells.<ref name=Kocak>Template:Cite journal</ref> The contrasting dye provides a clearer outline of abnormally-oriented blood vessels believed to be involved with the tumour. This is imperative for surgeons as it allows the patient's blood vessels to be mapped prior to operation.<ref name="Beck" />
Staging
The staging of renal cell carcinoma is the most important factor in predicting its prognosis.<ref name=cornellurology>Kidney Cancer / General Information Template:Webarchive at Weill Cornell Medical College, James Buchanan Brady Foundation, Department of Urology</ref> Staging can follow the TNM staging system, where the size and extent of the tumour (T), involvement of lymph nodes (N) and metastases (M) are classified separately. Also, it can use overall stage grouping into stage I–IV, with the 1997 revision of AJCC described below:<ref name=cornellurology/>
| Stage I | Tumour of a diameter of 7 cm (approx. 2 3⁄4 inches) or smaller, and limited to the kidney. No lymph node involvement or metastases to distant organs. |
| Stage II | Tumour larger than 7.0 cm but still limited to the kidney. No lymph node involvement or metastases to distant organs. |
| Stage III any of the following |
Tumor of any size with involvement of a nearby lymph node but no metastases to distant organs. Tumour of this stage may be with or without spread to fatty tissue around the kidney, with or without spread into the large veins leading from the kidney to the heart. |
| Tumour with spread to fatty tissue around the kidney and/or spread into the large veins leading from the kidney to the heart, but without spread to any lymph nodes or other organs. | |
| Stage IV any of the following |
Tumour that has spread directly through the fatty tissue and the fascia ligament-like tissue that surrounds the kidney. |
| Involvement of more than one lymph node near the kidney | |
| Involvement of any lymph node not near the kidney | |
| Distant metastases, such as in the lungs, bone, or brain. |
At diagnosis, 30% of renal cell carcinomas have spread to the ipsilateral renal vein, and 5–10% have continued into the inferior vena cava.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Histopathology


The gross and microscopic appearance of renal cell carcinomas is highly variable. Gross examination often shows a yellowish, multilobulated tumor in the renal cortex, which frequently contains zones of necrosis, haemorrhage and scarring. Microscopically, RCC is a heterogeneous group of cancers, made up of several distinct subtypes with different histologic features and clinical outcomes. The most common subtypes are clear cell, papillary, and chromophobe RCC. Sarcomatoid changes (morphology and patterns of IHC that mimic sarcoma, spindle cells) can be observed within any RCC subtype and are associated with more aggressive clinical course and worse prognosis.
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is the most prevalent subtype of renal cell carcinoma, accounting for approximately 75-80% of all cases.<ref name="cleveland-ccrcc">Template:Cite web</ref> The name is derived from the appearance of the tumor cells under a microscope, which look clear or pale due to a high content of glycogen and lipids that dissolves during tissue processing.
Pathophysiology and genetics
The development of ccRCC is strongly linked to the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 3p. Inactivation of the VHL gene, through mutation, deletion, or hypermethylation, is the hallmark of ccRCC and is found in over 90% of sporadic (non-inherited) cases.
The VHL protein is crucial for targeting hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) for degradation. When VHL is inactive, HIFs accumulate, leading to the overexpression of genes that promote tumor growth, angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels), and metastasis. This includes vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), which have become key targets for therapy.
While most cases are sporadic, ccRCC is the primary manifestation of Von Hippel–Lindau disease, a hereditary cancer syndrome that predisposes individuals to tumors in various organs, including the kidneys, brain, and pancreas.<ref name="cleveland-ccrcc"/>
Treatment and prognosis
For tumors confined to the kidney, surgery is the standard of care. This may involve a partial nephrectomy to preserve kidney function or a radical nephrectomy for larger tumors. For metastatic disease, treatment has been revolutionized by targeted therapy (e.g., sunitinib, cabozantinib) and immunotherapy (e.g., nivolumab, pembrolizumab), which target the VEGF pathway and stimulate the immune system, respectively.<ref name="cleveland-ccrcc"/> Prognosis is excellent for localized disease but is significantly poorer once the cancer has metastasized, though survival rates have improved with modern therapies.
Papillary renal cell carcinoma
Papillary renal cell carcinoma (pRCC) is the second most common subtype of RCC, accounting for 15-20% of all cases.<ref name="pathout-prcc">Template:Cite web</ref> It originates from the renal tubular epithelium and is characterized by a papillary or tubulopapillary architecture.
Histopathology and classification
Microscopically, pRCC tumors feature finger-like projections (papillae) with fibrovascular cores. It is common to find foamy macrophages, psammoma bodies (calcifications), and hemosiderin deposits within the tumor.
Historically, pRCC was divided into two subtypes:
- Type 1: Characterized by papillae covered with a single layer of small, basophilic cells with scant cytoplasm. These were generally considered to be lower grade and have a better prognosis.
- Type 2: Displayed papillae with larger, eosinophilic cells with prominent nucleoli, often arranged in a pseudostratified pattern. These were typically higher grade tumors with a worse prognosis.
However, the 2022 World Health Organization (WHO) classification of renal tumors no longer recommends this subtyping.<ref name="pathout-prcc"/> This change is due to significant morphologic variability, poor interobserver reproducibility, and the recognition that many tumors previously classified as "Type 2" are now considered distinct entities with specific genetic drivers (e.g., Fumarate hydratase-deficient RCC).
Genetics
pRCC is associated with distinct genetic alterations. Sporadic cases often show gains of chromosomes 7 and 17 and loss of the Y chromosome.<ref name="pathout-prcc"/>
Several hereditary syndromes are linked to pRCC:
- Hereditary papillary renal carcinoma (HPRC): This rare autosomal dominant syndrome is caused by germline mutations in the MET proto-oncogene on chromosome 7. It predisposes individuals to developing multiple, bilateral pRCC tumors, which are often slow-growing.<ref name="cancer-gov-prcc">Template:Cite web</ref>
- Hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer syndrome (HLRCC): This syndrome is caused by mutations in the fumarate hydratase (FH) gene. It is associated with a particularly aggressive form of pRCC, as well as cutaneous and uterine leiomyomas.<ref name="cancer-gov-prcc"/>
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment for localized pRCC is primarily surgical. For metastatic pRCC (mRCC), treatment has evolved from VEGFR inhibitors to more effective targeted therapies. Cabozantinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that targets MET and VEGFR, is considered a preferred option. Immunotherapy has also shown effectiveness.<ref name="pathout-prcc"/> In general, pRCC is associated with a better prognosis than clear cell RCC in patients without metastases, but prognosis is highly dependent on tumor stage and grade.
Grading
The recommended histologic grading schema for RCC is the Fuhrman system (1982), which is an assessment based on the microscopic morphology of a neoplasm with haematoxylin and eosin (H&E staining). This system categorises renal cell carcinoma with grades 1, 2, 3, 4 based on nuclear characteristics. The details of the Fuhrman grading system for RCC are shown below:<ref name=Rioux>Template:Cite journal</ref>
| Grade Level | Nuclear Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Grade I | Nuclei appear round and uniform, 10 μm; nucleoli are inconspicuous or absent. |
| Grade II | Nuclei have an irregular appearance with signs of lobe formation, 15 μm; nucleoli are evident. |
| Grade III | Nuclei appear very irregular, 20 μm; nucleoli are large and prominent. |
| Grade IV | Nuclei appear bizarre and multilobated, 20 μm or more; nucleoli are prominent. |
Nuclear grade is believed to be one of the most imperative prognostic factors in patients with renal cell carcinoma.<ref name="rini" /> However, a study by Delahunt et al. (2007) has shown that the Fuhrman grading is ideal for clear cell carcinoma but may not be appropriate for chromophobe renal cell carcinomas and that the staging of cancer (accomplished by CT scan) is a more favourable predictor of the prognosis of this disease.<ref name="Delahunt">Template:Cite journal</ref> In relation to renal cancer staging, the Heidelberg classification system of renal tumours was introduced in 1976 as a means of more completely correlating the histopathological features with the identified genetic defects.<ref name=Kovacs>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Prevention
The risk of renal cell carcinoma can be reduced by maintaining a normal body weight.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Management

The type of treatment depends on multiple factors and the individual, some of which include the stage of renal cell carcinoma (organs and parts of the body affected/unaffected), type of renal cell carcinoma, pre-existing or comorbid conditions and overall health and age of the person.<ref name=cohen /><ref name="simmons">Template:Cite book</ref> Every form of treatment has both risks and benefits; a health care professional will provide the best options that suit the individual circumstances.
If it has spread outside of the kidneys, often into the lymph nodes, the lungs or the main vein of the kidney, then multiple therapies are used including surgery and medications. RCC is resistant to chemotherapy and radiotherapy in most cases but does respond well to immunotherapy with interleukin-2 or interferon-alpha, biologic, or targeted therapy. In early-stage cases, cryotherapy and surgery are the preferred options.
Active surveillance
Active surveillance or "watchful waiting" is becoming more common as small renal masses or tumours are being detected and also within the older generation when surgery is not always suitable.<ref name="smaldone" /> Active surveillance involves completing various diagnostic procedures, tests and imaging to monitor the progression of the RCC before embarking on a more high risk treatment option like surgery.<ref name="smaldone">Template:Cite book</ref> In the elderly, patients with co-morbidities, and in poor surgical candidates, this is especially useful.
Surgery
Different procedures may be most appropriate, depending on circumstances.
The recommended treatment for renal cell cancer may be nephrectomy or partial nephrectomy, surgical removal of all or part of the kidney.<ref name="r"/> This may include some of the surrounding organs or tissues or lymph nodes. If cancer is only in the kidneys, which is about 60% of cases, it can be cured roughly 90% of the time with surgery.
Small renal tumors (< 4 cm) are treated increasingly by partial nephrectomy when possible.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Most of these small renal masses manifest indolent biological behavior with excellent prognosis.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Nephron-sparing partial nephrectomy is used when the tumor is small (less than 4 cm in diameter) or when the patient has other medical concerns such as diabetes or hypertension.<ref name="cohen" /> The partial nephrectomy involves the removal of the affected tissue only, sparing the rest of the kidney, Gerota's fascia and the regional lymph nodes. This allows for more renal preservation as compared to the radical nephrectomy, and this can have positive long-term health benefits.<ref name="pn vs rn weight">Template:Cite journal</ref> Larger and more complex tumors can also be treated with partial nephrectomy by surgeons with an extensive kidney surgery experience.<ref name="cw bjui">Template:Cite journal</ref>
Surgical nephrectomy may be "radical" if the procedure removes the entire affected kidney including Gerota's fascia, the adrenal gland which is on the same side as the affected kidney, and the regional retroperitoneal lymph nodes, all at the same time.<ref name="cohen" /> This method, although severe, is effective. But it is not always appropriate, as it is a major surgery that contains the risk of complication both during and after the surgery and can have a longer recovery time.<ref name="casey">Template:Cite journal</ref> It is important to note that the other kidney must be fully functional, and this technique is most often used when there is a large tumour present in only one kidney.
In cases where the tumor has spread into the renal vein, inferior vena cava, and possibly the right atrium, this portion of the tumor can be surgically removed, as well. When the tumor involved the inferior vena cava, it is important to classify which parts of the vena cava are involved and to plan accordingly, as sometimes complete resection will involve an incision into the chest with increased morbidity. For this reason, Dr. Gaetano Ciancio adapted liver mobilization techniques from liver transplant to address retrohepatic or even suprahepatic inferior vena caval thrombus associated with renal tumors.<ref name="Ciancio Livingstone Soloway 2007 pp. 988–995">Template:Cite journal</ref> With this technique, the whole abdominal inferior vena cava is able to be mobilized. This facilitates milking of the tumor down below the major hepatic veins by the surgeon's fingers, bypassing the need for a thoracoabdominal incision or cardiopulmonary bypass.<ref name="Ciancio Soloway 2005 pp. 266–270">Template:Cite journal</ref> In cases of known metastases, surgical resection of the kidney ("cytoreductive nephrectomy") may improve survival,<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> as well as resection of a solitary metastatic lesion. Kidneys are sometimes embolized prior to surgery to minimize blood loss.<ref name="pmid18380384">Template:Cite journal</ref>
Surgery is increasingly performed via laparoscopic techniques. Commonly referred to as key hole surgery, this surgery does not have the large incisions seen in a classically performed radical or partial nephrectomy, but still successfully removes either all or part of the kidney. Laparoscopic surgery is associated with shorter stays in the hospital and quicker recovery time but there are still risks associated with the surgical procedure. These have the advantage of being less of a burden for the patient and the disease-free survival is comparable to that of open surgery.<ref name="r"/> For small exophytic lesions that do not extensively involve the major vessels or urinary collecting system, a partial nephrectomy (also referred to as "nephron sparing surgery") can be performed. This may involve temporarily stopping blood flow to the kidney while the mass is removed as well as renal cooling with an ice slush. Mannitol can also be administered to help limit damage to the kidney. This is usually done through an open incision although smaller lesions can be done laparoscopically with or without robotic assistance.
Laparoscopic cryotherapy can also be done on smaller lesions. Typically a biopsy is taken at the time of treatment. Intraoperative ultrasound may be used to help guide placement of the freezing probes. Two freeze/thaw cycles are then performed to kill the tumor cells. As the tumor is not removed, followup is more complicated (see below) and overall disease-free rates are not as good as those obtained with surgical removal.
Surgery for metastatic disease: If metastatic disease is present surgical treatment may still a viable option. Radical and partial nephrectomy can still occur, and in some cases, if the metastasis is small this can also be surgically removed.<ref name=cohen /> This depends on what stage of growth and how far the disease has spread.
Percutaneous ablative therapies
Percutaneous ablation therapies use image-guidance by radiologists to treat localized tumors if a surgical procedure is not a good option. Although the use of laparoscopic surgical techniques for complete nephrectomies has reduced some of the risks associated with surgery,<ref name="Russo2013" /> surgery of any sort in some cases will still not be feasible. For example, the elderly, people who already have severe renal dysfunction, or people who have several comorbidities, surgery of any sort is not warranted.<ref name="Matin2013" />
A probe is placed through the skin and into the tumor using real-time imaging of both the probe tip and the tumor by computed tomography, ultrasound, or even magnetic resonance imaging guidance, and then destroying the tumor with heat (radiofrequency ablation) or cold (cryotherapy). These modalities are at a disadvantage compared to traditional surgery in that pathologic confirmation of complete tumor destruction is not possible. Therefore, long-term follow-up is crucial to assess completeness of tumour ablation.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Ideally, percutaneous ablation is restricted to tumours smaller than 3.5 cm and to guide the treatment. However, there are some cases where ablation can be used on tumors that are larger.<ref name="Matin2013" />
The two main types of ablation techniques that are used for renal cell carcinoma are radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation.<ref name="Matin2013" />
Radiofrequency ablation
Radiofrequency ablation uses an electrode probe which is inserted into the affected tissue to send radio frequencies to the tissue to generate heat through the friction of water molecules. The heat destroys the tumor tissue.<ref name="cohen" /> Cell death will generally occur within minutes of being exposed to temperatures above 50 °C.
Cryoablation
Cryoablation also involves the insertion of a probe into the affected area,<ref name="cohen" /> however, cold is used to kill the tumor instead of heat. The probe is cooled with chemical fluids which are very cold. The freezing temperatures cause the tumor cells to die by causing osmotic dehydration, which pulls the water out of the cell destroying the enzyme, organelles, cell membrane and freezing the cytoplasm.<ref name="Matin2013" />
Heavy ion radiotherapy
While RCC is traditionally considered highly radio-resistant, advanced forms of radiotherapy are emerging as promising treatments. Heavy ion radiotherapy, particularly with carbon ions (carbon ion radiotherapy, or CIRT), has shown significant potential due to its distinct physical and biological advantages over conventional photon (X-ray) radiation.<ref name="Zheng2024CIRT">Template:Cite journal</ref>
The primary physical advantage of CIRT is the Bragg peak, a phenomenon where the carbon ions deposit the vast majority of their energy precisely at the tumor site, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues. Biologically, heavy ions have a high linear energy transfer (LET), which causes complex and difficult-to-repair DNA double-strand breaks in cancer cells. This results in a higher relative biological effectiveness (RBE) for killing tumor cells, making it particularly effective against radio-resistant cancers like RCC.<ref name="Zheng2024CIRT"/>
Early clinical studies on CIRT for RCC, though limited, have reported excellent outcomes. For example, one study reported a 5-year local control rate of 100%, while another long-term follow-up showed a 94.1% local control rate.<ref name="Zheng2024CIRT"/> Furthermore, heavy ion therapy can induce immunogenic cell death, turning immunologically "cold" tumors "hot" and making them more susceptible to immune checkpoint inhibitors. This has led to growing interest in combining CIRT with immunotherapy to enhance systemic anti-tumor effects.<ref name="Zheng2024CIRT"/>
As of the mid-2020s, access to this advanced therapy is limited. Clinical heavy ion facilities are operational in several countries, including Japan, Germany, and China.<ref name="Pompos2022US">Template:Cite journal</ref> The United States, which discontinued its original program in 1993, is re-establishing its capabilities. The first new U.S. facility, at the Mayo Clinic in Florida, is expected to make carbon ion therapy clinically available in 2027 or later.<ref name="Pompos2022US"/><ref>Template:Cite news</ref>
Targeted drugs
Cancers often grow in an unbridled fashion because they are able to evade the immune system.<ref name=":0"/> Immunotherapy is a method that activates the person's immune system and uses it to their own advantage.<ref name=":0"/> It was developed after observing that in some cases there was spontaneous regression due to natural activity of the immune system.<ref name="davar">Template:Cite book</ref> Immunotherapy capitalises on this phenomenon and aims to increase a person's immune response to cancer cells.<ref name="davar" /> Other targeted therapy medications inhibit growth factors that have been shown to promote the growth and spread of tumours.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref name="stroup">Template:Cite book</ref> Most of these medications were approved within the past ten years.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> These treatments are:<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Template:Div col
- Nivolumab<ref name=Quinn2015>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- Axitinib<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- Sunitinib<ref name="MotzerHutson2007">Template:Cite journal</ref>
- Cabozantinib<ref name=Quinn2015/>
- Everolimus
- Ipilimumab<ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
- Lenvatinib
- Pazopanib
- Bevacizumab
- Sorafenib
- Tivozanib
- Temsirolimus<ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
- Interleukin-2 (IL-2) has produced "durable remissions" in a small number of patients, but with substantial toxicity.<ref>Renal Cell Carcinoma MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Retrieved on 2010-09-10</ref>
- Interferon-α
For patients with metastatic cancer, sunitinib probably results in more progression of the cancer than pembrolizumab, axitinib and avelumab.<ref name=":1">Template:Cite journal</ref> In comparison to pembrolizumab and axitinib, it probably results in more death, but it may slightly reduce serious unwanted effects.<ref name=":1" /> When compared with combinations of immunotherapy (nivolumab and ipilimumab), sunitinib may lead to more progression and serious effects.<ref name=":1" /> There may be little to no difference in progression, survival and serious effects between pazopanib and sunitib.<ref name=":1" />
Activity has also been reported for ipilimumab<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> but it is not an approved medication for renal cancer.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref>
More medications are expected to become available in the near future as several clinical trials are being conducted for new targeted treatments,<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> including: atezolizumab, varlilumab, durvalumab, avelumab, LAG525, MBG453, TRC105, and savolitinib.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy and radiotherapy are not as successful in the case of RCC. RCC is resistant in most cases but there is about a 4–5% success rate, but this is often short-lived with more tumours and growths developing later.<ref name=cohen />
Adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy
Adjuvant therapy, which refers to therapy given after a primary surgery, had for a long time not been found to be beneficial in renal cell cancer.<ref name="nejm" /> However, in 2021 Pembrolizumab was approved for adjuvant treatment after showing promising disease-free survival improvements.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Conversely, neoadjuvant therapy is administered before the intended primary or main treatment. In some cases neoadjuvant therapy has been shown to decrease the size and stage of the RCC to then allow it to be surgically removed.<ref name="stroup" /> This is a new form of treatment and the effectiveness of this approach is still being assessed in clinical trials. It is noteworthy that response of renal cell carcinoma patients to immunotherapy can be governed by a number of factors, including but not limited to, antigen presentation capacity, immunogenic features of the tumours, pro-inflammatory cross-talk between macrophages and T cells as well as specific clinico-pathological features.<ref name="Nat Med">Template:Cite journal</ref>
Metastasis
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) is the spread of the primary renal cell carcinoma from the kidney to other organs. Approximately 25–30% of people have this metastatic spread by the time they are diagnosed with renal cell carcinoma.<ref name="DoisMissing">Template:Cite journal</ref> This high proportion is explained by the fact that clinical signs are generally mild until the disease progresses to a more severe state.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> The most common sites for metastasis are the lymph nodes, lung, bones, liver and brain.<ref name="motzer" /> How this spread affects the staging of the disease and hence prognosis is discussed in the "Diagnosis" and "Prognosis" sections.
MRCC has a poor prognosis compared to other cancers, although average survival times have increased in the last few years due to treatment advances. Average survival time in 2008 for the metastatic form of the disease was under a year,<ref name="DoictrvMissing" /> and by 2013 this improved to an average of 22 months.<ref name="DoiCADbeecMissing">Template:Cite journal</ref> Despite this improvement the five-year survival rate for mRCC remains under 10%<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> and 20–25% of patients remain unresponsive to all treatments and in these cases, the disease has a rapid progression.<ref name="DoiCADbeecMissing" />
The available treatments for RCC discussed in the "Treatment" section are also relevant for the metastatic form of the disease. Options include interleukin-2, which is a standard therapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma.<ref name="nejm" /> From 2007 to 2013, seven new treatments have been approved specifically for mRCC (sunitinib, temsirolimus, bevacizumab, sorafenib, everolimus, pazopanib and axitinib).<ref name=singer /> These new treatments are based on the fact that renal cell carcinomas are very vascular tumours – they contain a large number of blood vessels. The drugs aim to inhibit the growth of new blood vessels in the tumours, hence slowing growth and in some cases, reducing the size of the tumours.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Side effects are quite common with these treatments and include:<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
- Gastrointestinal effects – nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia
- Respiratory effects – coughing, dyspnea (difficulty breathing)
- Cardiovascular effects – hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Neurological effects – intracranial hemorrhage (bleeding into the brain), thrombosis (blood clots) in the brain
- Effects on the skin and mucous membranes – rashes, hand-foot syndrome, stomatitis
- Bone marrow suppression – resulting in reduced white blood cells, increasing the risk of infections plus anemia and reduced platelets
- Renal effects – impaired kidney function
- Fatigue
Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are more commonly used in the metastatic form of RCC to target the secondary tumours in the bones, liver, brain and other organs. While not curative, these treatments provide relief for symptoms associated with the spread of tumours.<ref name="DoiCADbeecMissing" />
Prognosis
The prognosis is influenced by several factors, including tumour size, degree of invasion and metastasis, histologic type, and nuclear grade.<ref name="rini"/> Staging is the most important factor in predicting the outcome of renal cell cancer. The following numbers are based on patients first diagnosed in 2001 and 2002 by the National Cancer Data Base:<ref>Kidney Cancer (Adult) – Renal Cell Carcinoma. Template:Webarchive. American Cancer Society. Retrieved on 2010-09-10.</ref>
| Stage | Description | 5 Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| I | Confined to the kidney | 81% |
| II | Extend through the renal capsule, confined to Gerota's Fascia | 74% |
| III | Include the renal vein, perinephric fat or the hilar lymph nodes | 53% |
| IV | Includes tumors that are invasive to adjacent organs (except the adrenal glands), or distant metastases | 8% |
A Korean study estimated a disease-specific overall five-year survival rate of 85%.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> Taken as a whole, if the disease is limited to the kidney, only 20–30% develop metastatic disease after nephrectomy.<ref>[1] Template:Webarchive Renal Cancer Causes, Symptoms, Treatment. eMedicine Health. Retrieved on 2010-09-10</ref> More specific subsets show a five-year survival rate of around 90–95% for tumors less than 4 cm. For larger tumors confined to the kidney without venous invasion, survival is still relatively good at 80–85%.<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> For tumors that extend through the renal capsule and out of the local fascial investments, the survivability reduces to near 60%.Template:Citation needed Factors as general health and fitness or the severity of their symptoms impact the survival rates. For instance, younger people (among 20–40 years old) have a better outcome despite having more symptoms at presentation, possibly due to lower rates spread of cancer to the lymph nodes (stage III).
Histological grade is related to the aggressiveness of the cancer, and it is classified in 4 grades, with 1 having the best prognosis (five-year survival over 89%), and 4 with the worst prognosis (46% of five-year survival).
Some people have the renal cell cancer detected before they have symptoms (incidentally) because of the CT scan (Computed Tomography Imaging) or ultrasound. Incidentally diagnosed renal cell cancer (no symptoms) differs in outlook from those diagnosed after presenting symptoms of renal cell carcinoma or metastasis. The five-year survival rate was higher for incidental than for symptomatic tumours: 85.3% versus 62.5%. Incidental lesions were significantly lower stage than those that cause symptoms, since 62.1% patients with incidental renal cell carcinoma were observed with Stage I lesions, against 23% were found with symptomatic renal cell carcinoma.<ref name="pmid10647646">Template:Cite journal</ref>
If it has metastasized to the lymph nodes, the five-year survival is around 5% to 15%. For metastatic renal cell carcinoma, factors which may present a poor prognosis include a low Karnofsky performance-status score (a standard way of measuring functional impairment in patients with cancer), a low haemoglobin level, a high level of serum lactate dehydrogenase, and a high corrected level of serum calcium.<ref name=Motzer1>Template:Cite journal</ref><ref name=Motzer2>Template:Cite journal</ref> For non-metastatic cases, the Leibovich scoring algorithm may be used to predict post-operative disease progression.<ref name=Leibovich>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Renal cell carcinoma is one of the cancers most strongly associated with paraneoplastic syndromes, most often due to ectopic hormone production by the tumour. The treatment for these complications of RCC is generally limited beyond treating the underlying cancer.
Epidemiology
The incidence of the disease varies according to geographic, demographic and, to a lesser extent, hereditary factors. There are some known risk factors, however the significance of other potential risk factors remains more controversial. The incidence of the cancer has been increasing in frequency worldwide at a rate of approximately 2–3% per decade<ref name="DoictrvMissing">Template:Cite journal</ref> until the last few years where the number of new cases has stabilised.<ref name="Ljungberg et al 2011">Template:Cite journal</ref>
The incidence of RCC varies between sexes, ages, races and geographic location around the world. Men have a higher incidence than women (approximately 1.6:1)<ref name="nejm">Template:Cite journalTemplate:Dead link</ref> and the vast majority are diagnosed after 65 years of age.<ref name="nejm" /> Asians reportedly have a significantly lower incidence of RCC than whites and while African countries have the lowest reported incidences, African Americans have the highest incidence of the population in the United States.<ref name="Ljungberg et al 2011" /> Developed countries have a higher incidence than developing countries, with the highest rates found in North America, Europe and Australia / New Zealand.<ref>Template:Cite book</ref>
History
Daniel Sennert made the first reference suggesting a tumour arising in the kidney in his text Practicae Medicinae, first published in 1613.<ref name=history>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Miril published the earliest unequivocal case of renal carcinoma in 1810.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref> He described the case of Françoise Levelly, a 35-year-old woman, who presented to Brest Civic Hospital on April 6, 1809, supposedly in the late stages of pregnancy.<ref name=history />
Koenig published the first classification of renal tumours based on macroscopic morphology in 1826. Koenig divided the tumors into scirrhous, steatomatous, fungoid and medullary forms.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Hypernephroma controversy
Following the classification of the tumour, researchers attempted to identify the tissue of origin for renal carcinoma.
The pathogenesis of renal epithelial tumours was debated for decades. The debate was initiated by Paul Grawitz when in 1883, he published his observations on the morphology of small, yellow renal tumours. Grawitz concluded that only alveolar tumours were of adrenal origin, whereas papillary tumours were derived from renal tissue.<ref name=history />
In 1893, Paul Sudeck challenged the theory postulated by Grawitz by publishing descriptions of renal tumours in which he identified atypical features within renal tubules and noted a gradation of these atypical features between the tubules and neighboring malignant tumour. In 1894, Otto Lubarsch, who supported the theory postulated by Grawitz coined the term hypernephroid tumor, which was amended to hypernephroma by Felix Victor Birch-Hirschfeld to describe these tumours.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Vigorous criticism of Grawitz was provided by Oskar Stoerk in 1908, who considered the adrenal origin of renal tumours to be unproved. Despite the compelling arguments against the theory postulated by Grawitz, the term hypernephroma, with its associated adrenal connotation, persisted in the literature.<ref name=history />
Foot and Humphreys, and Foote et al. introduced the term Renal Celled Carcinoma to emphasize a renal tubular origin for these tumours. Their designation was slightly altered by Fetter to the now widely accepted term Renal Cell Carcinoma.<ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
Convincing evidence to settle the debate was offered by Oberling et al. in 1959 who studied the ultrastructure of clear cells from eight renal carcinomas. They found that the tumour cell cytoplasm contained numerous mitochondria and deposits of glycogen and fat. They identified cytoplasmic membranes inserted perpendicularly onto the basement membrane with occasional cells containing microvilli along the free borders. They concluded that these features indicated that the tumours arose from the epithelial cells of the renal convoluted tubule, thus finally settling one of the most debated issues in tumour pathology.<ref name=history /><ref>Template:Cite journal</ref>
See also
- Dysuria
- Interferon
- Interleukin-2
- Kidney cancer
- Knudson hypothesis<ref name="Valladares2008" />
- Rapamycin
- Stauffer syndrome
- Vinblastine
- Vasculogenic Mimicry
References
External links
Template:Medical resources Template:Urologic neoplasia Template:Tumor morphology Template:Authority control